In bypass motors, the working air is independent from the cooling air. A separate fan directly cools the motor armature and field. Usually the cooling air enters and exists through slots in the equipment housing.
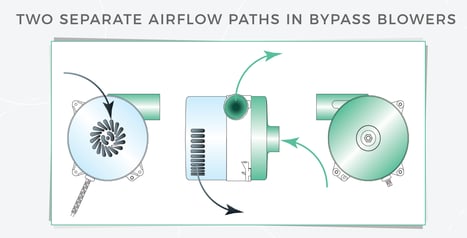
Bypass blowers are electric-motor-driven blowers that segregate two paths of air:
- Working Air: The path of air for performing the application’s blowing or vacuum function.
- Cooling Air: The path of air to cool the blower’s motor during operation.
Bypass Blower Benefits
- The air-moving technology provides higher performance and cooler working-air temperature as well as cleaner air through the motor space.
- There is dedicated airflow to the motor and drive and also improved thermal management so the blowers can output higher torque-speed values.
- The blowers run at cooler temperatures, which extends the life of the blower.
More specifically, bypass blowers may be the only choice where industrial, HVAC, and appliance applications need cool working air. In applications with demanding duty cycles, blowers can generate significant heat. If this heat is insufficiently shed, temperatures can quickly rise and cause premature blower shutdown.
Bypass blowers excel where the working air threatens to contaminate or wet the motor and its electronics
Bypass blowers are also indispensable wherever working air has contaminants that threaten to accumulate on the motor-controller electronics within the blower. This contamination can cause electrical short circuits and failure by overheating. Consider the extreme case of blowers in floor-cleaning equipment. Here, bypass blowers allow for scrubber and carpet-extraction functions that involve the vacuuming of water and debris.
What’s the difference between a bypass blower and a bypass motor?
There is no difference between a bypass blower and a bypass motor. A bypass motor is common in industries where it’s understood that the overall motor-driven design serves a blower function. In fact, bypass blowers are made in brushed and brushless motor designs, as the need for air separation (if not its specific form) is independent of other design variations. AMETEK Windjammer®, Lamb® and Nautilair® products all come in bypass-blower designs to serve various applications requiring the prevention of air mixing.
What’s the difference between a peripheral and a tangential blower?
Peripheral blowers and tangential blowers are the two different subtypes of bypass motors. Both blower subtypes have a round-cylinder design to accommodate the rotating circular fan, but other design features differ in how the air exits the motor.
Peripheral bypass blowers deliver diffuse air discharge — uncontrolled into the environment or chamber being treated. On a typical peripheral bypass blower, instead of a horn for air discharge, there are small louvres on the side of the cylinder itself. Instead of being directed out, air exits as if it’s leaking out of the cylinder.
Peripheral bypass blowers excel where focused output-air direction is unimportant. One advantage is that the design is relatively compact, especially useful in designs or tight enclosures with geometry that can’t accommodate tubes or other air-routing components.
Another common peripheral bypass blower application is with redesigns, where a machine builder must replace a peripheral bypass blower because that’s what the machine was originally designed to accommodate. Here, it is increasingly common to replace brush motor variations (still the dominant peripheral-bypass motor option) with brushless motor variations to obtain longer design life.
In contrast, tangential-bypass blowers include a horn to force air to exit the blower at a direction at a right angle to the air-inlet direction.
In fact, most blower applications use tangential bypass blowers. That’s because tangential blowers have the advantage of letting designers route blower output to specific directions, or even out through a tube. For the latter, designs often include a round output tube onto which a hose can mount to. This allows routing of discharge air to very specific volumes within a machine or environment.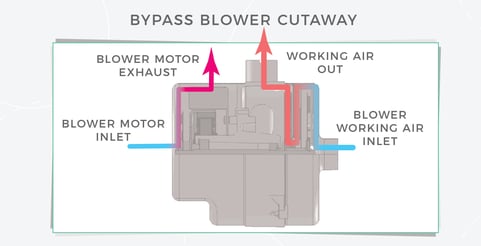
At AMETEK Dynamic Fluid Solutions, we understand you’re looking for more than just an off-the-shelf part or one-time solution. You need a true technology partner who understands your engineering challenge that is focused on you, providing customized, collaborative solutions. We’ll also provide you with excellent customer service for a great total experience.






